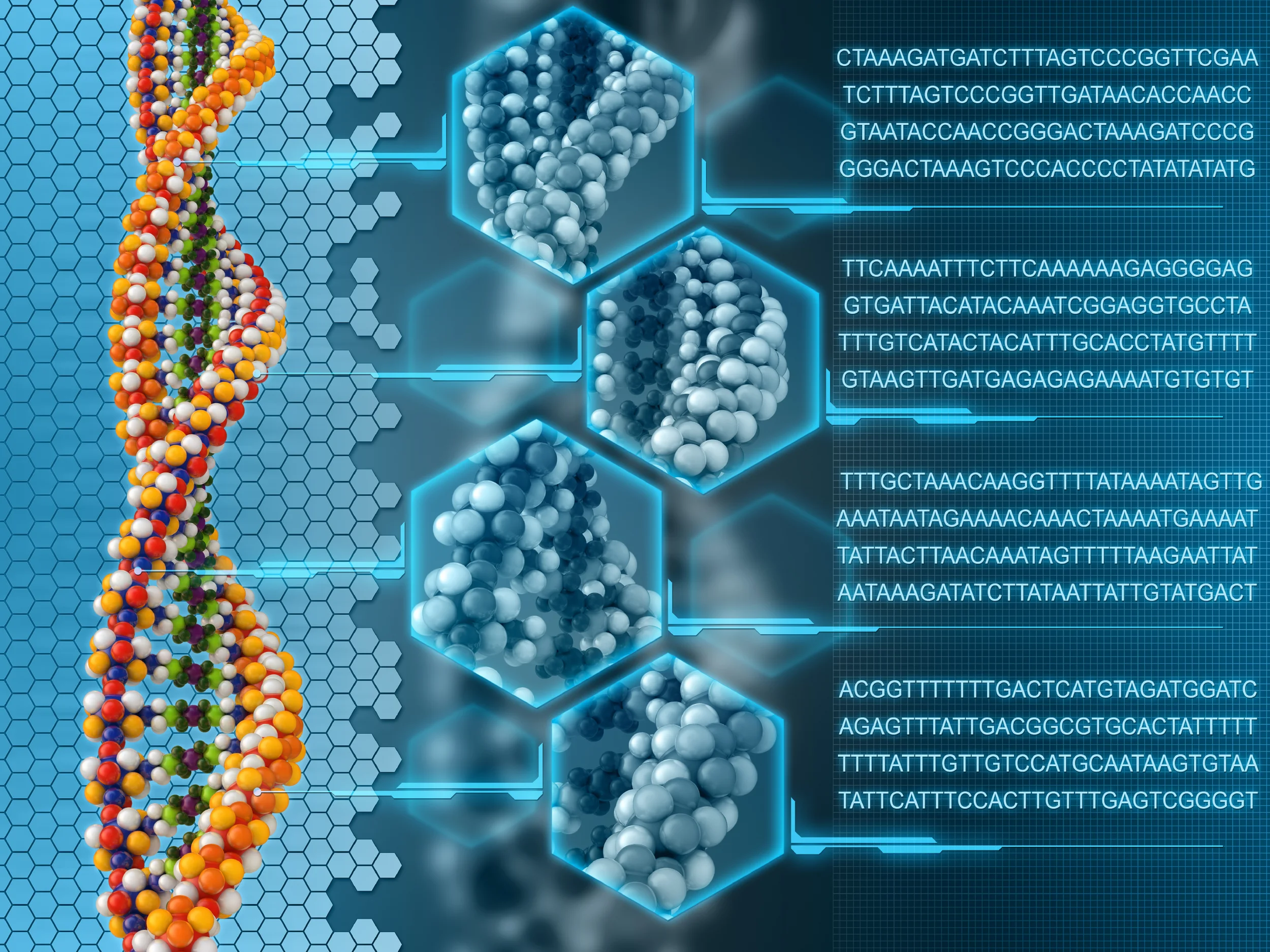
What is DNA? What is a gene? What is a mutation?
In brief, DNA is a long molecule that stores information. DNA is located in the centre (nucleus) of every cell and contains all the instructions necessary for the organism to function. Similar to pearls on a necklace, along the DNA strand there are millions of basic structural units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide (pearl) is one of four types: A, T, G or C, as determined by the nitrogenous base they contain, i.e., nucleotide 'A' has Adenine, 'T' has Tyrosine, 'C' has Cysteine and 'G' has Guanine. These four types of...